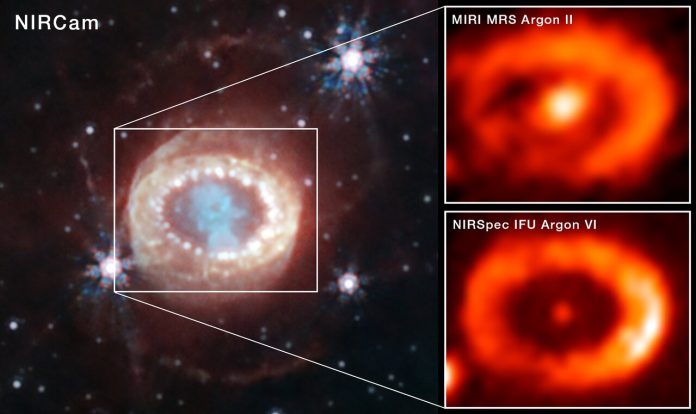
In a study reported recently, astronomers observed the SN 1987A remnant using 제임스 웹 우주 망원경(JWST). The results showed emission lines of ionized argon and other heavily ionised chemical species from the centre of the nebula around SN 1987A. Observation of such ions means presence of a newly born neutron 별 as the source of high energy radiation at the centre of the supernova remanent.
별 are born, age and finally die with an explosion. When the fuel runs out and nuclear fusion in the core of star ceases, the inward gravitational force squeezes the core to contract and collapse. As the collapse begins, in few milliseconds, the core gets so compressed that electrons and protons combine to form neutrons and a neutrino is released for each neutron formed. In the case of 초대형 별,핵은 강력하고 빛나는 폭발로 짧은 시간 안에 붕괴됩니다. 초신성. The burst of neutrinos produced during core-collapse escape into outer 공간 unimpeded due to its non-interactive nature with matter, ahead of photons which are trapped in the field, and acts as a beacon or an early warning of a possible optical observation of supernova explosion soon
SN 1987A was the last supernova event seen in southern sky in February 1987. It was the first such supernova event visible to the naked eye since Kepler’s in 1604. Located 160 000 light-years from Earth in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud (a satellite 은하 of the Milky Way), it was one of the brightest exploding stars seen in more than 400 years that blazed with the power of 100 million suns for several months and provided unique opportunity to study the phases before, during, and after the death of a 별.
The SN 1987A was a core-collapse supernova. The explosion was accompanied by neutrino emission which was detected by two water Cherenkov detectors, Kamiokande-II and the Irvine-MichiganBrookhaven (IMB) experiment about two hours prior to the optical observation. This suggested that a compact object (a neutron star or 블랙홀) should have formed after core collapse, but no neutron star following SN 1987A event or any other such recent supernova explosion was ever directly detected. Though, there is indirect evidence for presence of a neutron star in the remanent.
In a study reported recently, astronomers observed the SN 1987A remnant using 제임스 웹 우주 망원경(JWST). The results showed emission lines of ionized argon and other heavily ionised chemical species from the centre of the nebula around SN 1987A. Observation of such ions means presence of a newly born neutron star as the source of high energy radiation at the centre of the supernova remanent.
젊은 중성자별에서 나오는 높은 에너지 방출의 영향이 감지된 것은 이번이 처음입니다.
***
출처 :
- Fransson C., et al 2024. 초신성 1987A의 잔해에 있는 소형 물체에서 나오는 전리 방사선으로 인한 방출선. 과학. 22년 2024월 383일. 6685권, 898호, 903-XNUMX페이지. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adj5796
- 스톡홀름 대학. 뉴스 - 제임스 웹 망원경이 상징적인 초신성에서 중성자별의 흔적을 탐지합니다. 22년 2024월 XNUMX일. https://www.su.se/english/news/james-webb-telescope-detects-traces-of-neutron-star-in-iconic-supernova-1.716820
- ESA. News-Webb은 젊은 초신성 잔해의 중심에서 중성자별에 대한 증거를 발견했습니다. 다음에서 이용 가능 https://esawebb.org/news/weic2404/?lang
***