The Laser Interferometer 스페이스 버튼 Antenna (LISA) mission has received the go ahead of European 스페이스 버튼 Agency (ESA). This paves the way for developing the instruments and spacecrafts commencing January 2025. The mission is led by ESA and is a result of collaboration between ESA, its Member State 공간 기관, NASA, and an international consortium of scientists.
Scheduled to be launched in 2035, LISA will be the first 공간기반 중력파 observatory dedicated to detection and study of millihertz ripples caused by distortions in the fabric of 공간-시간 (중력파) 건너편에 우주.
Unlike the ground based 중력파 detectors (LIGO, VIRGO, KAGRA, and LIGO India) which detect 중력파 in frequency range of 10 Hz to 1000 Hz, LISA will be designed to detect 중력파 of much longer wavelengths in the low frequency range between 0.1 mHz and 1 Hz.
초저주파(10- 9- 10- 8 헤르츠) 중력파 (GWs) with wavelengths from weeks to years from supermassive binary 블랙홀 can be detected using ground-based 펄서 타이밍 어레이(PTA)). However, low frequency 중력파 (GWs) with frequency between 0.1 mHz and 1 Hz can neither be detected by LIGO nor by Pulsar Timing Arrays (PTAs) – the wavelength of these GWs is too long for LIGO and too short for PTAs to detect. Hence, the need for 공간-based GW detector.
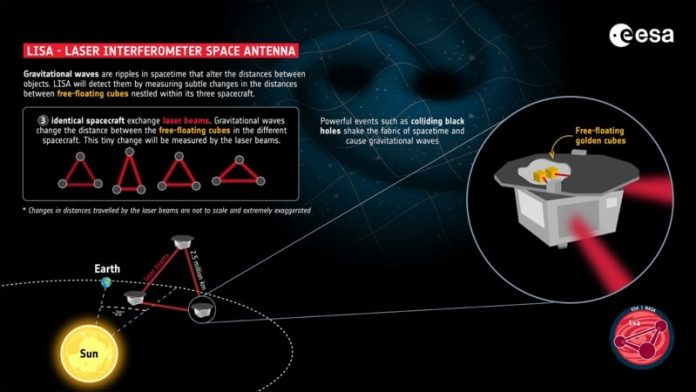
LISA will be a constellation of three spacecrafts in accurate equilateral triangle formation in space. Each side of the triangle will be 2.5 million km long. This formation (of the three spacecrafts) will 궤도 Sun in an Earth-trailing heliocentric 궤도 between 50 and 65 million km from Earth while maintaining a mean inter-spacecraft separation distance of 2.5 million km. This space-based configuration makes LISA an extremely large detector to study low frequency 중력파 that ground-based detectors can not.
For detection of GWs, LISA will use pairs of test masses (solid gold-platinum cubes) free-floating in special chambers at the heart of each spacecraft. 중력 ripples will make extremely small changes in the distances between test masses in the spacecrafts which will be measured through laser interferometry. As demonstrated by LISA Pathfinder mission, this technology is capable of measuring changes in distances to a few billionths of a millimetre.
LISA will detect GWs caused by merger of supermassive 블랙홀 at the centre of galaxies thus will shed light on evolution of galaxies. The mission should also detect the predicted gravitational '울리는' 초기 순간에 형성되었습니다. 우주 빅뱅 후 처음 몇 초 안에.
***
참조 :
- ESA. 뉴스 - 시공간 파급력 포착: LISA가 앞서 나갑니다. 게시일: 25년 2024월 XNUMX일. 사용 가능 위치: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Capturing_the_ripples_of_spacetime_LISA_gets_go-ahead
- NASA. 리사. 다음에서 이용 가능 https://lisa.nasa.gov/
- Pau Amaro-Seoane et al. 2017. Laser Interferometer 스페이스 버튼 Antenna. Preprint arXiv. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1702.00786
- Baker et al. 2019. The Laser Interferometer 스페이스 버튼 Antenna: Unveiling the Millihertz Gravitational Wave Sky. Preprint arXiv. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1907.06482
***
***
***